Product Description
Product spections :
| Interchange number: | 1345A090 |
| MITUSUBISHI |
Description :
1. The tensioner is a belt tensioner used in the automobile transmission system. The tension pulley is mainly composed of a fixed shell, a tension arm, a wheel body, a torsion spring, a rolling bearing and a spring sleeve. It can automatically adjust the tension force according to the different tightness of the belt to make the transmission system stable, safe and reliable.
2. The main function of the tensioner bearing is to support the mechanical rotating body.
3.Reduce the friction coefficient during its movement and ensure its rotation accuracy.
4.Change sliding friction into rolling friction.
| 2018 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2018 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SEL Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2018 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2018 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2018 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SEL Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2018 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SEL Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SEL Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | GT Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | GT Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SEL Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2017 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SEL Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SEL Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | GT Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SEL Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | GT Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sportback Hatchback 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sportback Hatchback 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 3.0L 2998CC 182Cu. In. V6 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | DE Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sportback Hatchback 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sportback Hatchback 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | GT Sportback Hatchback 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | SE Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Outlander | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.4L 2360CC 144Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | LE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | DE Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sedan 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Mitsubishi | Lancer | ES Sportback Hatchback 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | ES Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Mitsubishi | Outlander Sport | SE Sport Utility 4-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
The benefits of using pulleys
A pulley is a mechanical device that converts force into rotation. There are many advantages to using pulleys. Let’s take a look at a few of them. This article will describe the advantages, types, applications, and power sources of pulleys. You can then choose the pulley that best suits your specific needs. If you’re looking for a new tool to help you with a certain task, this article is for you.
Mechanical advantage
The mechanical advantage of a pulley can be defined as the ratio of applied force to the applied force. The mechanical advantage of a pulley can be calculated by considering several factors, including weight and friction. It can be calculated by the force applied per unit length of rope and the number of pulleys used. In a single-circuit system, the force required to lift a heavy object is equal to the user’s body weight.
The mechanical advantage of a pulley can be realized by comparing it to a seesaw. Both uses of rope are suitable for lifting objects. A rope 4 times heavier than a kilo is 4 times as effective. Because the forces on both sides of the pulley are equal, a small force is enough to move a large weight a short distance. The same force can be applied to a large mass to lift it several meters.
After introducing the concept of mechanical advantage, learners will practice using the pulley system. In addition to testing the pulley system, they should also calculate its mechanical advantage. Using either the instructor-provided handout or the learner’s workbook, students will determine how easily the pulley system functions. Once they have completed the test, they can discuss their results and how the system can be improved. These courses are best completed as part of a mini-unit or as a standalone main course.
The mechanical advantage of the pulley system is proportional to the number of rope loops. This circuit requires the same force as the dual circuit to lift heavy objects. A single lap requires only a third of the force to lift a double lap, while 3 laps require almost half the energy required for a single lap. The mechanical advantage of the pulley system becomes constant as the number of cycles increases.
The 3:1 Mechanical Advantage system feels like lifting a 300-pound load with 3 feet of rope. The three-foot-long rope moves the load 1 foot high. Understanding the mechanical advantages of pulleys is critical for rescuers when trying to create the perfect pulley system. Ideally, the pulley system will be anchored to a nearby rock, tree, pole or person – if the weight is not too heavy.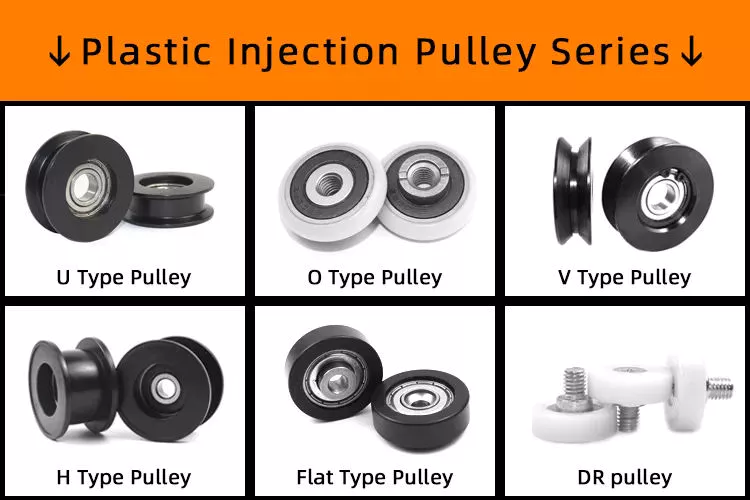
Types of pulleys
There are several types of pulleys. V-belt pulleys are the type commonly used in vehicles and electric motors. “V” pulleys require a “V” belt, and some even have multiple V grooves. “V” pulleys are often used in heavy duty applications for power transmission because they reduce the risk of power slippage.
Composite pulleys combine the properties of fixed and movable pulleys. Compound pulleys are able to change the direction of force while requiring relatively low force to move even the heaviest loads. Mechanical advantage is a measure of the effectiveness of a machine or equipment. It can be divided into 3 categories: force, distance and mechanics. Once you understand how each type works, you can design complex machines.
Fixed pulleys: These pulleys are the most basic type of pulleys. They use ropes and slotted wheels to move with the lifted object. Because they are so simple to set up, lifting heavy objects is a breeze. Although the moving object feels light, it is actually heavier than it actually is. These pulleys are used in construction cranes, utility elevators and many different industries.
Compound Pulley System: A pulley pulley is a combination of 2 fixed pulleys and 1 movable pulley. Compound pulley systems are effective for moving heavy objects because they have the largest force multipliers and are flexible enough to change the direction of the force as needed. Composite pulley systems are commonly used in rock climbing, theater curtains and sailing. If you’re looking for a pulley system, you can start by evaluating the types of pulleys and their uses.
Construction Pulleys: These are the most basic types of pulleys and have wheel rails. These pulleys can be lifted to great heights and attached to chains or ropes. They allow workers to access equipment or materials from greater heights. They are usually mounted on wheels with axles and secured with ropes. They are essential tools for construction workers. There are many different types of pulleys out there.
energy source
Belts and pulleys are mechanical devices used to transmit energy and rotational motion. The belt is connected to the rotating part of the energy source, and the pulley is mounted on the other. One pulley transmits power to the other, while the other changes the direction of the force. Many devices use this combination, including automobiles, stationary generators, and winches. It is used in many home applications, from conveyors to treadmills. Pulleys are also used for curtains in theater halls.
Pulley systems are an essential part of modern industry and everyday life. Pulleys are used in elevators, construction sites and fitness equipment. They are also used in belt-driven generators as backup power. Despite their simple and seemingly humble beginnings, they have become a versatile tool. From lifting heavy objects to guiding wind turbines, pulley systems are widely used in our daily lives.
The main reason why pulleys are so popular is the mechanical advantage they offer. They can lift a lot of weight by applying very little force over longer distances. For example, a small motor can pull 10 meters of cable, while a large motor can pull 1 meter. Also, the work done is equal to the force times the distance traveled, so the energy delivered to the large motor is the same.
The power source for the pulley system can be cables, belts or ropes. The drive element in a pulley system is usually a rope or cable. A belt is a loop of flexible material that transmits motion from 1 pulley to another. The belt is attached to the shaft and a groove is cut in the pulley. The belt then transfers energy from 1 pulley to the other through the system.
application
A pulley is a mechanical device used to lift heavy objects. They reduce the amount of work required to lift heavy objects and are an excellent choice for many applications. There are several different applications for pulleys, including elevators, grinders, planters, ladder extensions, and mountaineering or rock climbing. Let’s take a look at some of the most popular uses for pulleys in modern society. These include:-
A pulley is a mechanical device that changes force. To use, you wrap the rope around it and pull down to lift the object. While this device is very useful, a major limitation of using pulleys is that you still have to apply the same force to lift the object as you would without the pulleys. This is why people use pulleys to move large objects like furniture and cars.
In addition to lifting heavy objects, pulleys are used in elevators, flagpoles and wells. These systems allow people to move heavy objects without straining their backs. Many other examples of pulleys in the home include garage doors, flagpoles, and elevators. They also help raise and lower flagpoles, which can reach several stories high.
There are 2 basic types of pulleys: movable and fixed. Fixed pulleys are attached to a ceiling or other object using 2 ropes. Modern elevators and construction cranes use movable pulleys, as do some weight machines in gyms. Composite pulleys combine movable and fixed pulleys to minimize the force required to move heavy objects.
Another type of fixed pulley is the flagpole. A flagpole can support a country, organization, or anything else that needs to be lifted. A taller flagpole creates a prouder moment for those who support it. The operation of the rope and pulley mechanism is very simple. The user simply attaches the flag to the rope, pulls the pulley, and he or she can watch the flag rise and unfold.

